Does your skin look thinner, less bouncy, and more tender? There is no question that the thickness of your skin changes with age. Little by little, your skin feels drier, more tender and less elastic. And with thinner skin comes a weakened skin barrier. When the skin is healthy, it successfully does its job of protecting us from irritation, skin diseases and inflammation. But when our skin barrier is weakened, the body cannot defend itself. We'll explore how thin and weak skin can affect the skin barrier and repair methods to make the skin healthier and stronger.
Why is my skin so thin?
aging
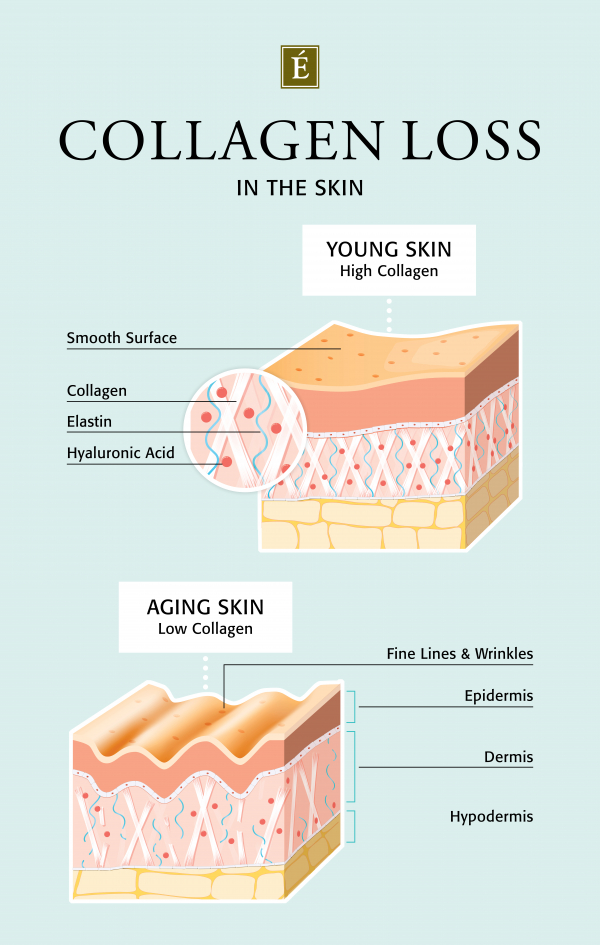
As you get older, you may notice changes in the texture and elasticity of your skin. The reason your skin can appear thinner and drier is because your body makes less collagen as you age. Collagen is the structural protein that gives the skin elasticity, firmness and suppleness. Collagen fibers are the stable pillars that support the top layer of skin and prevent sagging skin. But with the decline in collagen, skin becomes thinner and less supple. You can thank your genetics for how quickly your collagen supply is depleting.

Lifestyle factors including medication
As Healthline suggests, long-term use of certain medications can cause you to develop thin skin, including:
- Prescription blood thinners
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen (Advil) or naproxen (Aleve)
- Topical and oral corticosteroids
- Over-the-counter aspirin
There are also a number of lifestyle factors that can lead to early aging and thinning of the skin, including:
- smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Lack of regular exercise combined with a poor diet high in sugar and refined carbohydrates
Sun exposure
Excessive exposure to ultraviolet light causes sun damage to your skin, and after many years of tanning (and burning) you can begin to develop thinning skin. Sun damage can also take the form of age spots, sagging skin, wrinkling, or skin cancer. You may notice thinning skin on your face, arms, or hands, the parts of your body that are most exposed to the sun.
How does thin skin affect me?
Thin skin doesn't cause medical problems – it's only a problem if your skin bruises easily or is damaged. As Medline Plus notes, “As you age, there is an increased risk of skin damage. Your skin is thinner, more fragile, and you lose some of the protective layer of fat. ”The skin's ability to snap back worsens with age, as does the thickness of the dermis. And bruises and wrinkles appear on thin skin.
If you take care of your skin in addition to your thinning skin, its barrier can be compromised. The skin consists of three layers: The subcutaneous layer consists of sweat glands, fat and tissue. The next layer is called the dermis, which is made up of the blood supply and nerves. The outermost layer is the epidermis, which forms your skin barrier and protects you from bacteria and dirt. A healthy, functioning skin barrier blocks environmental stimuli while retaining natural oils and moisture. An unhealthy skin barrier doesn't protect you from potential skin problems like irritation, inflammation, or dryness. Thin skin is already sensitive enough, but if you don't hydrate very dry skin or exfoliate too much, you can irritate it. If you want to learn more about what causes a damaged skin barrier, read this in-depth guide. Here's a breakdown of the practical ways you can achieve stronger, thicker skin.
How to make the skin stronger and thicker
Eat foods that support collagen production
It has been shown repeatedly that omega-3 fatty acids are essential for increasing collagen production and thus strengthening our skin and improving the barrier function of our skin. Vitamin C also plays an important role in collagen and you can find it in foods like broccoli, leafy greens, and citrus fruits.
A variety of foods can help your body increase collagen production, including:
- chicken
- Leafy vegetables
- Berry
- Fish and shellfish
- protein
- Citrus fruits
Use skin care products that contain peptides
If you are already satisfied with your diet, you can use skin care products that contain peptides to strengthen your skin. Dermatologist Dr. Nancy Samolitis, MD, FAAD told Byrdie, “Peptides are essentially fragmented parts of proteins. So when used in skin care, the goal is for these collagen fragments to stimulate collagen growth … Whole, non-fragmented proteins (like collagen) cannot be absorbed directly through the top layer of skin, leaving those smaller pieces deep inside can penetrate the cellular level. "
Apply moisturizer daily
To strengthen your skin, shift your attention from exfoliating to moisturizing instead. Whether you are a dry, mixed, oily or sensitive skin type, hydrating your skin is the first step towards healthy skin and a strong skin barrier.
Your dehydration could be genetic; You might just be born with a dry skin type. However, if your skin type is indeed oily, mixed, sensitive, or normal, dryness from air conditioning or hot showers to the weather can be the cause. Help your skin stay strong by applying a moisturizer after cleansing. This step helps lock in moisture and protect your skin from the elements.
In the following video our Lead Skin Care Trainer Natalie Pergar has some moisturizer recommendations for every skin type.
(embed) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OPXO1mpvGy0 (/ embed)
Are you struggling with thinning skin? Have you tried any of the above tips or other treatments for this problem? Learn more about the Marine Flower Peptide Collection with powerful plant peptides and sea flower technology for stronger, firmer and firmer skin.